 Introduction
Introduction
Wetting is the adsorption of liquid at a solid surface. The process is important in coatings and inks, for example when solid particles must be dispersed in a liquid medium or when a liquid paint or ink is applied on a substrate.
Pre-condition for wetting
In the following, we concentrate on wetting of a flat solid substrate by a liquid paint or ink. The two properties that govern whether or not complete wetting will take place are the surface tension of the liquid γlg and the surface energy of the substrate γsg1. Complete wetting of a flat solid surface will occur when the surface tension of the liquid is lower than the surface energy of the solid: γlg < γsg. This precondition is often called the wetting condition for flat surfaces.
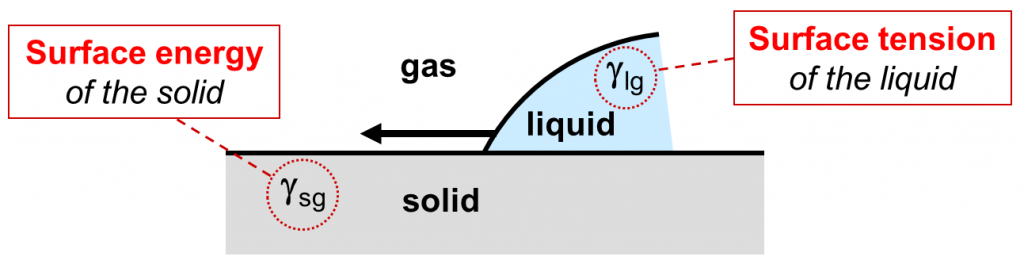
Wetting agents
Wetting agents are additives that are used to improve wetting behavior of paints and inks. To be more precise, wetting agents lower the surface tension of a liquid so that the complete system, consisting of solid and liquid, complies with the wetting condition. Wetting agents have a surfactant structure, implying that the molecules have a hydrophilic part and a hydrophobic part2. Nonionic wetting agents do not carry a charge. The hydrophilic part of anionic wetting agents carries a negative charge in water-based systems.
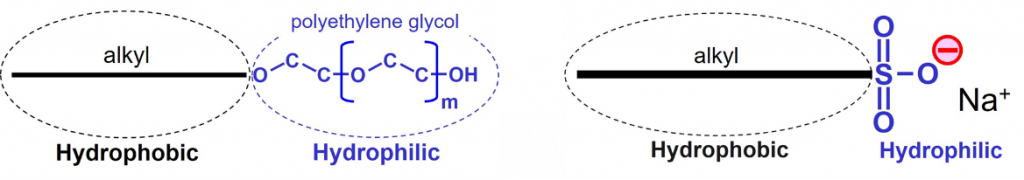
Wetting agents lower the surface tension of a liquid because the surfactant molecules adsorb and orient at the liquid-air interface in such a way that the hydrophobic tails point towards the air.

Wetting agents are especially important in water-based systems. The reason for this is that water is a liquid with high surface tension: γlg of water is 73 mJ/m2 at room temperature1.
Challenges and innovations
A range of challenges, related to the use of wetting agents in water-based systems, are well known. I address two of them. First, many wetting agents stabilize foam bubbles. This problem can be solved by using defoamers. However, defoamers themselves often cause problems like cratering and orange peel. Secondly, the wetting agent molecules must move to the liquid-air interface as fast as possible when application of the system has stopped. It is said that the equilibrium surface tension (EST) must be obtained in a short time. It will come as no surprise that the industry is looking for innovative wetting agents that obtain EST as fast as possible and do not give foam problems.
An example
A concept used to make wetting agents with low foam sensitivity is the Gemini structure3. A molecule that has Gemini structure contains, for example, 2 hydrophilic hydroxyl (-OH) groups and two hydrophobic tails (R2 and R3).
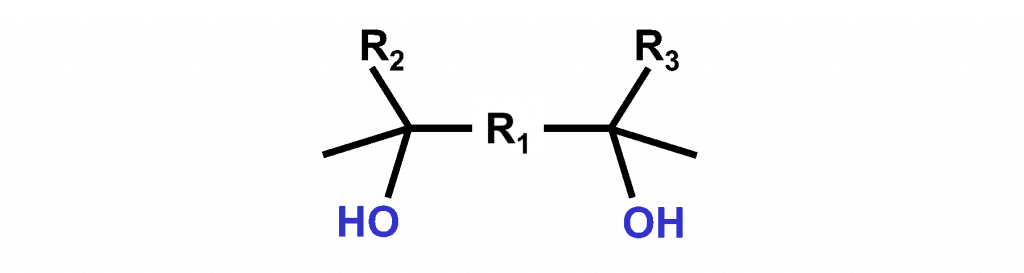
Surfynol® 107 L is a nonionic alkane diol surfactant having Gemini structure. The additive is particularly suitable as wetting agent for water-based systems. The molecules adsorb fast at the water-air interface and they have a tendency to destabilize foam bubbles.
References
- Article Surface Tension & Surface Energy, Jochum Beetsma, 27 September 2019.
- Article Lowering surface tension – Surfactants in coating materials, Marc Hirsch, 25 February 2021.
- Article Sticking to the Subject about superwetters for waterbased systems, Roger Reinartz et al., European Coatings Journal, issue 7/8 of 2015, page 20-25.
The views, opinions and technical analyses presented here are those of the author or advertiser, and are not necessarily those of ULProspector.com or UL Solutions. The appearance of this content in the UL Prospector Knowledge Center does not constitute an endorsement by UL Solutions or its affiliates.
All content is subject to copyright and may not be reproduced without prior authorization from UL Solutions or the content author.
The content has been made available for informational and educational purposes only. While the editors of this site may verify the accuracy of its content from time to time, we assume no responsibility for errors made by the author, editorial staff or any other contributor.
UL Solutions does not make any representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy, applicability, fitness or completeness of the content. UL Solutions does not warrant the performance, effectiveness or applicability of sites listed or linked to in any content.



Leave a Reply or Comment